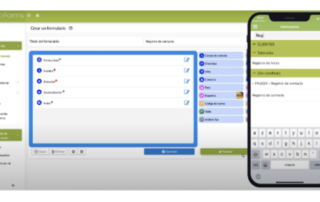
What is Digitization?
It is a system by which field work is performed to update and build physical systems (supply networks, rainwater, electricity, street furniture, etc.) taking the data that the client wants to know and transferring them to a 3D digital BIM model for the processing of this data in a massive way (BIG DATA).

Thanks to digitization, a model is created where all the data of a physical system is centralized in a visual way, enabling intelligent and optimized asset management.
Allowing:
-To carry out procedures with other administrations in a more agile way (legalization of discharge points, network capacity analysis in order to have more clients, etc.).
-To manage future investments in an intelligent way.
-Manage maintenance efficiently.
How does it work?
The digitization process consists of 3 steps.
- Step 1: Analysis of existing data and field data collection.
- Step 2: BIM modeling and information input into the model.
- Step 3: Data analysis.
Step 1: Data collection
Step 1: Data collection
Step 1 is made up of two parts:
- Contact (meeting with the client)
- What is the baseline data the client has?
- What information would the client like to know about the system?
- Data collection campaign design based on the client’s needs.
- Optimization of data collection with technologically advanced tools (less time, less cost).
- Technical qualified staff.
Step 2: Modeling and data input
Step 2: Modeling and data input
Automatic BIM modeling from field data
Custom programming script
– Automatically models nodes directly from field data
– Puts metadata to modeled elements
Manual modeling
– Those elements that require interpretation

Step 3: Data analysis
Step 3: Data analysis
Outcome:
- Customized reports with the data that the client wishes to know
- Training in the use of the model
- Technical assistance for data handling.
- Support and advice to the client until the end of the project.
What is it used for?
Having a centralized 3D information model with all the data of a network’s assets opens up a range of possibilities as broad as the client wants to exploit it.
Same examples are:
BIM Methodology:
- Customized visual reports, personalized to the client’s needs for intelligent decision-making.
- Use Clash-Detection tools for interference with other affected new construction utilities.
- Preparation of hydraulic calculations (in case of rainwater supply or water supply networks).
Maintenance management:
- The modeled database can be loaded into a maintenance management system (CAMM).
- Creation of maintenance campaigns based on the actual state of the network.
- Possibility to plan maintenance work in a simulated virtual environment.
Environmental Services:
- Mapping of wastewater dumping into the networks to manage their legalization.
- Study of the correct uses made by users of the networks.
- Planning of a campaign, for telematic auscultation of the networks (pollutants, pressure in the network, leak detection, etc.).